
In the following example, the note D has been chromaticized in a different way. It’s important to understand this scale because it is the progression of notes that all other patterns are created from. Indeed, knowing how the tune “ought” to sound, the funky sound of the D# sounds accidental. The chromatic scale is the most basic scale in music. Plus, the C sounds so good against the E chord anyway, so it’s doubly. So the C adds a half-step-away alternative for the blues-scale D that clashes with the A-chord C. The major third, C, is a half step away from the D in the scale.

Because the note D# does not belong to the key of C major, it is considered a chromatic alteration of the melody. The notes A and E (the one and the five of the chord) are already in the E blues scale (E, G, A, Bb, B, D). The “#” symbol (called a sharp) indicates that a note is to be played one half step higher than in the original version.

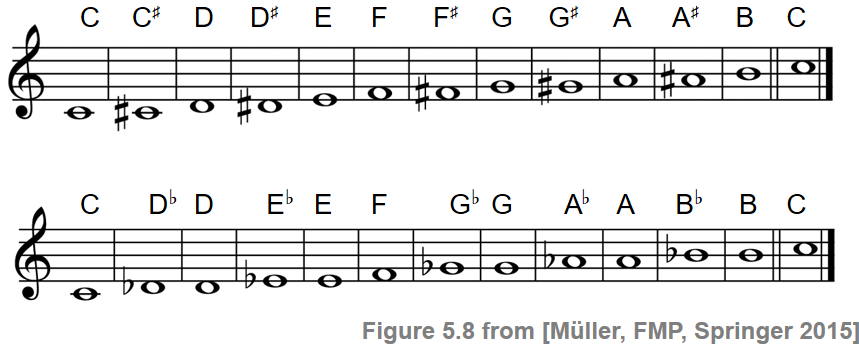
In the example below, the note D has been replaced with one of its chromatic inflections: D has been replaced with D#. ) Here are the C major scale and a chromatic scale that begins on the note C.Ĭhromatic Scale that begins on the note Cįor an illustration of the first meaning, we might imagine some modified versions of the Yankee Doodle melody: (An earlier method used to indicate accidentals involved notating inflected pitches in colors other than black – a practice reflecting the origins of the use of “chromatic” for scales containing these inflected pitches. A chromatic note is indicated in music notation using a set of symbols called “accidentals placed beside notes to indicate how they should be inflected – typically raised (“sharped”) or lowered (“flatted”). (ii) to describe a twelve-note scale that contains all the notes available in the Western pitch system (i.e., a scale that uses all the “white keys” and all the “black keys”). (i) to describe notes that fall outside the seven-note scale associated with each of the twenty-four major or minor keys The following video explains how such a scale is formed and.
#Chromatic notes how to#
First we will deal with diatonic and chromatic substitution notes, which are the main means of obscuring conventional chords.As applied to music, the word “chromatic”, derived from the Greek word for color,is typically used in one of two ways: At grade 4 you will be expected to understand how to write and recognise chromatic scales. On Friday, Chroma Gallery, located downtown at Barnard and Congress streets on Ellis Square, will host an open house reception for its newest exhibition, 'Chromatic Notes.' Three of the gallerys.It possesses a complete chromatic scale between these two notes.In layman’s terms, this means all the notes. Officially, the chromatic scale is a twelve-tone scale starting on a root note and moving by half-steps only. In layman’s terms, a chromatic scale is all the notes. We choose what to omit, and that creates new scales. The movement falls into two repeated halves, the second having more chromatic lower parts. It’s from the chromatic scale that all other scales in western music emerge.Power, a New Zealander, plays the blues harp and the chromatic harmonica.
#Chromatic notes code#
The new system was as deep and mysterious as its chromatic code name implied.In my next column I will deal with the chromatic approach notes.Featuring a color wheel of free-form music notes. Substitution notes may be diatonic or chromatic. Keep your badge, passkey, phone, or backstage pass close at hand with this chromatic scale for your neck.From Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English Related topics: Music, Colours chromatic chro‧mat‧ic / krəʊˈmætɪk, krə- $ kroʊ-, krə- / adjective 1 APM technical related to a musical scale which consists of semitone s a chromatic scale chromatic harmonies 2 CC formal related to bright colours Examples from the Corpus chromatic


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
